With the widespread adoption of smoking alternatives, Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs) and E-cigarettes have become highly regarded choices. While both aim to offer safer alternatives to traditional cigarettes, they significantly differ in operation principles, user experience, and health impacts. This article delves into the distinctions between HTPs and e-cigarettes, aiding consumers in better understanding and selecting the product that suits them.
I. Operation Principles
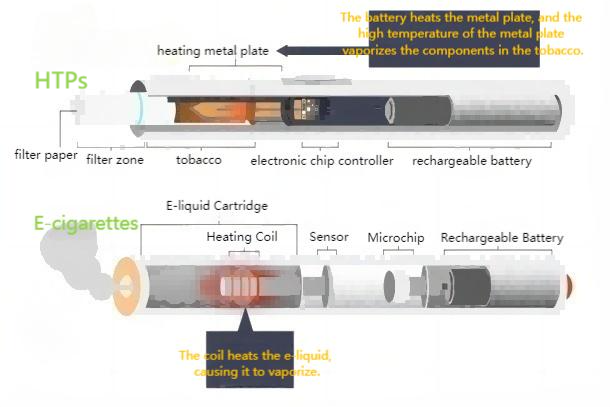
Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs): The fundamental principle of HTPs involves heating tobacco instead of burning it to release nicotine and other aromatic compounds. Typical HTP devices include a heater and specially designed tobacco sticks (such as IQOS's HeatSticks). The heater heats the tobacco stick to about 300°C, generating vapor rather than combustion, thereby reducing the release of harmful substances.
Electronic Cigarettes (e-cigarettes): E-cigarettes operate by heating E-liquidwith a battery-driven heating element to produce aerosol for inhalation. E-liquids typically contain nicotine, propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, and various flavor additives. E-cigarette devices vary widely, ranging from disposable small devices to rechargeable high-end equipment.
II. User Experience
Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs):
-
Similar to traditional smoking: The use and sensation of heated tobacco products (HTPs) are closer to traditional cigarettes because they utilize actual tobacco leaf. This makes the transition more natural for users accustomed to traditional smoking.
-
Temperature control: HTP devices typically feature precise temperature control, ensuring a consistent experience with each use.
-
Residue: After using HTPs, there is some tobacco residue that needs to be cleaned.
Electronic Cigarettes (e-cigarettes):
- Diverse flavor options: Electronic cigarettes offer a variety of flavor choices, ranging from traditional tobacco flavors to fruity, dessert, and other diversified options, catering to different consumer preferences.
- Adjustability: Advanced electronic cigarette devices allow users to adjust nicotine concentration, aerosol output, and other settings, providing a personalized vaping experience.
- No tobacco residue: After use, electronic cigarettes do not leave behind any tobacco residue to clean up; instead, users only need to periodically replace the e-liquid or cartridges.
III. Health Effects
Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs):
- Reduced Harmful Substances:Due to the absence of combustion, heated tobacco products release significantly lower levels of harmful substances such as carbon monoxide and tar compared to traditional cigarettes. However, there are still some harmful chemicals present that require further research to determine their long-term effects.
- Nicotine Content::The nicotine content in heated tobacco products is similar to that of traditional cigarettes, hence the addictive potential is comparable.
Electronic Cigarettes (e-cigarettes):
- Risk of Chemical Components:Electronic cigarettes produce aerosols containing propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, and various chemical flavorings. While they generally contain fewer harmful substances compared to traditional cigarettes, the long-term health effects of inhaling these chemicals still require further research.
- Risk of Explosion and Leakage:Some low-quality electronic cigarette devices pose risks of battery explosions or e-liquid leakage. Users should choose products from reputable brands to mitigate these risks.
IV. Regulation and Legislation
Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs): Many countries impose stringent regulations on heated tobacco products, requiring them to undergo extensive health and safety testing before they can be marketed. Additionally, some countries have strict restrictions on their sale and advertising.
Electronic Cigarettes (e-cigarettes): The regulation of electronic cigarettes varies by country. Some countries enforce strict regulations on e-cigarettes, including requirements for product ingredient labeling, advertising limitations, and sales regulations. In contrast, other countries have relatively relaxed policies, allowing for unrestricted sale and advertising.
V. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs): After use, heated tobacco products generate tobacco residues and disposable tobacco sticks, which require proper disposal to reduce environmental pollution.
Electronic Cigarettes (e-cigarettes): Electronic cigarette devices are typically reusable; however, the disposal issues of e-liquid bottles and disposable cartridges still need attention. Additionally, the handling of batteries in e-cigarette devices poses an environmental challenge.
Conclusion
Heated tobacco products and E-cigarettes serve as alternatives to traditional cigarettes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Heated tobacco products offer an experience closer to traditional smoking but still involve actual tobacco leaves. On the other hand, electronic cigarettes provide a variety of flavors and more flexibility in usage, though their long-term health effects require further research. When choosing between these two products, consumers should make informed decisions based on their personal preferences, health considerations, and regulatory information.

